elisa test which disease|elisa test positive means : makers Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay - or ELISA for short - is a laboratory technique or assay where antibodies or antigens in people’s samples are immobilized in a surface, and then detected by an antibody with an enzyme attached that causes a change of color.. So it’s useful to diagnose infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B, or malaria; and autoimmune diseases, like Graves’ . $15.99
{plog:ftitle_list}
$1,373.00
ELISA test is commonly used to detect P24 antigen (HIV diagnosis), HBsAg (diagnosis of hepatitis B), influenza virus antigen detection, and rota-virus antigen detection. Indirect ELISA test detects specific viral antibodies against hepatitis C virus, Chikungunya virus, Zika virus, human T-cell lymphotropic virus, and HIV in the patient’s serum.The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological assay commonly used to measure antibodies, antigens, proteins and glycoproteins in biological samples. Some examples include: diagnosis of HIV infection, pregnancy tests, and measurement of cytokines or soluble receptors in cell supernatant or serum.
ELISA test results, what does a positive ELISA test tell you? . Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced in pregnancy, 25 can be detected by ELISA in urine samples. Autoimmune disease. Markers indicative of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis 26 and lupus 27 may be detected and quantified by ELISA. ELISA tests find widespread applications in clinical laboratories and research settings. They are employed for diagnosing various diseases and conditions, such as infections like HIV, detecting autoimmune disorders, and identifying allergic responses, including food allergies.ELISA tests are also used in the pharmaceutical industry for drug development and .Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay - or ELISA for short - is a laboratory technique or assay where antibodies or antigens in people’s samples are immobilized in a surface, and then detected by an antibody with an enzyme attached that causes a change of color.. So it’s useful to diagnose infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B, or malaria; and autoimmune diseases, like Graves’ .
As with antibody tests for other infectious diseases, the accuracy of these tests depends upon how long you've been infected. Antibody tests may appear falsely negative during the first few weeks of infection, typically when a patient has an erythema migrans rash, but FDA-cleared assays have good sensitivity after 4-6 weeks have passed. An ELISA test uses components of the immune system (such as IgG or IgM antibodies) and chemicals for the detection of immune responses in the body. The ELISA test involves an enzyme (a protein that catalyzes a biochemical reaction). . and some allergic diseases like food allergies. ELISA tests are also known as immunosorbent assays. Following . ELISA remains one of the most important immunological techniques in modern medicine. There are four types of ELISA that include direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive ELISA. They are employed in different situations in the diagnosis of diseases in the laboratory.
If Lyme disease is still suspected in people with a negative ELISA who were tested within 4 weeks from symptom onset, repeat the ELISA 4 to 6 weeks after the first ELISA test. 1.2.18. If Lyme disease is still suspected in people with a negative ELISA who have had symptoms for 12 weeks or more, perform an immunoblot test. 1.2.19.Indirect Detection Tests. Antibody-based tests (ELISA, IFA, Western blot, Immunoblot): These tests detect antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi in the blood or spinal fluid. This is the most commonly ordered set of tests for Lyme disease.The first-tier Lyme disease screening enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) used is the Zeus ELISA Borrelia VlsE1/pepC10 IgG/IgM test system. The Zeus ELISA Borrelia VlsE1/pepC10 IgG/IgM test system is designed to detect IgG- and IgM-class antibodies (not differentiated by the assay in the final result) in human sera to VlsE1 and pepC10 .
The ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) test for Lyme disease is a blood test designed to detect antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease. This test serves as the initial step in diagnosing Lyme disease. How it’s Used. The ELISA test screens for antibodies against B. burgdorferi.
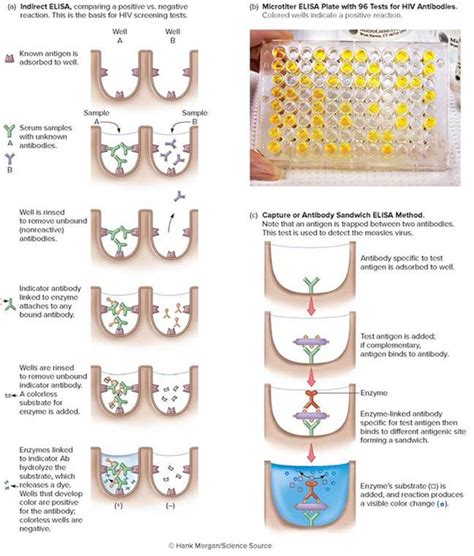
reasons for positive elisa tests
It is a commonly used laboratory test to detect antibodies in the blood. An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful . ELISA blood test ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunoassay. . Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed .These tests are generally more sensitive and specific than the Western Blot, ELISA and IFA tests. Learn more about these Lyme disease tests that IGENEX offers. Other Lyme Disease Tests. Three other tests that may be used to diagnose Lyme disease are polymerase chain reaction (PCR), antigen detection and culture testing. The most common Lyme disease blood tests. The two most common diagnostic tests for Lyme disease are the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and the Western blot. These Lyme disease tests allow physicians to visualize the reaction between antibodies in an infected person’s blood to specific antigens or parts of the bacteria that cause . Only a positive Western blot test can confirm the diagnosis of Lyme disease. For many people, the ELISA test remains positive, even after they have been treated for Lyme disease and no longer have symptoms. A positive ELISA test may also occur with certain diseases not related to Lyme disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis. .
ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunoassay. It is a commonly used laboratory test to detect antibodies in the blood. An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. The CDC recommends that doctors first order an ELISA to screen for Lyme disease and then confirm Lyme disease with a Western blot. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test detects antibodies to B. burgdorferi. Studies show that the ELISA test generates false negative results approximately half of the time.
Direct tests lack sensitivity for Lyme disease; hence, serologic tests remain the gold standard. Currently recommended is a standard 2-tier testing strategy using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) followed by Western blot for confirmation.
The diagnosis of Chagas disease, particularly in the chronic phase, is based on the detection of specific IgG antibodies against Trypanosoma cruzi, with the ELISA test being the most common in laboratories, and immunochromatographic tests or rapid diagnostic tests (RDT) the most common in primary health care centers or field screening studies.ELISA is used to detect the presence and to quantify specific antigens or antibodies. ELISA being an immunoassay method is very sensitive and specific in nature whereby the specific antigens or antibodies bind to their homologous antibodies and antigens, respectively. Overview of ELISA Test. ELISA is performed on a Microtitre plate. A . What is ELISA? The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an antibody-based technique for the detection and quantification of target analytes in solution. The targets are typically proteins, for example, cytokines, chemokines, immunoglobulins, hormones, and other biomarkers. ELISA setups include direct/indirect (antigen first), competitive, and sandwich . ELISA tests. ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ELISA tests can be used to see if a patient has any antibodies to a certain antigen (or any antigens to a certain antibody) For example, they can be used to test for infections by pathogens or for allergies; In an ELISA test: An enzyme is attached to antibodies
The ELISA test detects the presence of antibodies in the blood, essentially categorizing normal from abnormal results. Measures are broken down into numbers, with results greater than or equal to 1.0 indicating potential infection. This test may be less effective in the early going—since antibodies may not have formed—but is very sensitive. Interpretation of Lyme disease results from RIPL Negative ELISA on serum. Early clinical Lyme disease in the form of erythema migrans with an associated history of a tick bite should be treated . Wampole Bb (IgG/IgM) ELISA test system FDA and MarDx Lyme Disease (IgG and IgM) Marblot Strip Test System FDA/HC: BSK culture (plasma >9ml) 1: 19.2: n/a: Open in a separate window. a PA = positive agreement estimate = On a sample of clinical LD patients, this is the probability of test 2 being positive if test 1 is positive. enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), biochemical procedure in which a signal produced by an enzymatic reaction is used to detect and quantify the amount of a specific substance in a solution. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) typically are used to detect antigens, though they can also be used to detect other substances, including .
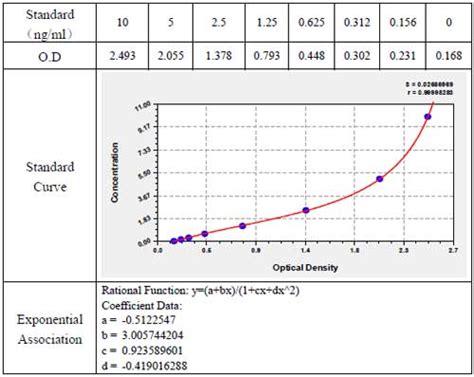
elisa test results explained
$481.16
elisa test which disease|elisa test positive means